Bootstrap Media queries Override
Overview
Like we talked previously in the modern-day net that gets viewed pretty much in the same way through mobile phone and desktop gadgets having your webpages adjusting responsively to the display screen they get displayed on is a must. That is certainly why we have the effective Bootstrap system at our side in its latest fourth edition-- currently in development up to alpha 6 produced at this moment.
But what is this aspect beneath the hood which it literally applies to do the job-- just how the page's material becomes reordered as needed and just what helps make the columns caring the grid tier infixes just like
-sm--md-Exactly how to utilize the Bootstrap Media queries Grid:
The responsive behaviour of one of the most famous responsive system inside its own newest 4th version comes to function thanks to the so called Bootstrap Media queries Css. Things that they execute is having count of the width of the viewport-- the display of the gadget or the width of the browser window in case the web page gets displayed on desktop and employing various designing regulations properly. So in common words they follow the simple logic-- is the width above or below a certain value-- and pleasantly activate on or off.
Each viewport size-- such as Small, Medium and so on has its own media query determined except for the Extra Small screen dimension that in newest alpha 6 release has been certainly employed universally and the
-xs-.col-xs-6.col-6The general syntax
The standard format of the Bootstrap Media queries Using Override in the Bootstrap framework is
@media (min-width: ~ breakpoint in pixels here ~) ~ some CSS rules to be applied ~@media (max-width: ~ breakpoint in pixels here ~) ~ some CSS ~Other detail to consider
Exciting thing to observe right here is that the breakpoint values for the different display screen scales differ through a specific pixel depending to the regulation that has been used like:
Small-sized display sizes -
( min-width: 576px)( max-width: 575px),Medium display scale -
( min-width: 768px)( max-width: 767px),Large size screen size -
( min-width: 992px)( max-width: 591px),And Extra large display sizes -
( min-width: 1200px)( max-width: 1199px),Responsive media queries breakpoints
Considering Bootstrap is designed to be mobile first, we make use of a number of media queries to create sensible breakpoints for formats and user interfaces . These particular breakpoints are typically based on minimum viewport widths and enable us to graduate up factors just as the viewport changes. ( read here)
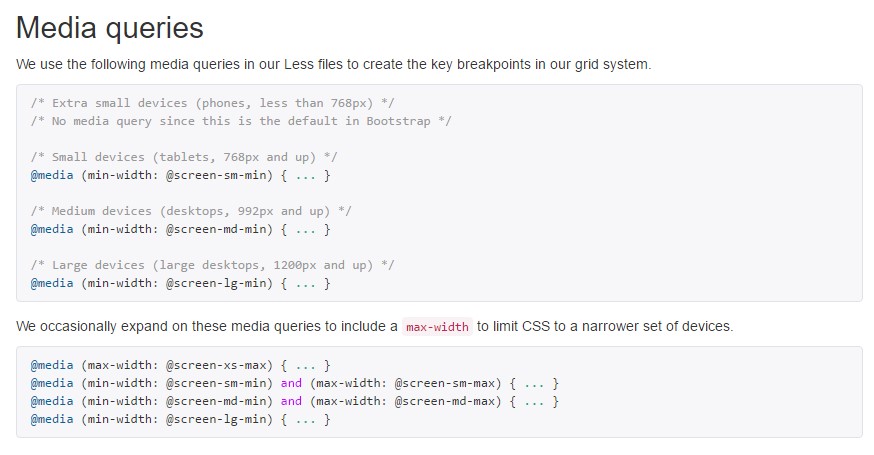
Bootstrap mainly uses the following media query varies-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass data for design, grid program, and elements.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Due to the fact that we create resource CSS in Sass, every media queries are readily available by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We sometimes employ media queries which go in the other route (the granted display scale or even more compact):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce again, these types of media queries are likewise provided with Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for targeting a particular part of display screen scales employing the minimum and maximum breakpoint widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Such media queries are as well readily available via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Likewise, media queries may span several breakpoint sizes:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for focus on the exact same display dimension range would certainly be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Final thoughts
Do notice again-- there is simply no
-xs-@mediaThis upgrade is aiming to brighten up both of these the Bootstrap 4's design sheets and us as web developers due to the fact that it observes the natural logic of the way responsive content functions rising right after a specific spot and together with the losing of the infix there actually will be much less writing for us.
Look at a couple of youtube video guide about Bootstrap media queries:
Related topics:
Media queries formal documents
Bootstrap 4: Responsive media queries breakpoints

Bootstrap 4 - Media Queries Tactics
